:quality(80))
Semiconductor Jobs Skills Radar 2026: Emerging Tools, Platforms & Techniques to Learn Now
As chip demand surges across AI, automotive, defence, 5G and consumer electronics, the UK’s semiconductor sector is undergoing a resurgence. With new government investment and domestic R&D growing, employers are looking for engineers and technicians who understand the tools, design flows, and fabrication technologies powering modern chip development.
Welcome to the Semiconductor Jobs Skills Radar 2026—your annual guide to the software, simulation tools, lab techniques, and platforms most in demand across the UK semiconductor industry. Whether you’re a silicon design engineer, process technician or verification expert, this guide helps you keep your skillset aligned with real hiring needs.
Why Semiconductor Skills Are Evolving in 2026
UK employers are increasingly looking for hybrid talent that can:
Bridge hardware and software in embedded SoC environments
Use RTL design and verification workflows fluently
Operate cleanroom equipment or understand fab process flows
Apply signal and power integrity principles in high-speed design
Automate EDA and verification with Python, Tcl, and shell scripting
Demand is growing across digital design, analogue simulation, RF, packaging, yield optimisation, and device reliability. Startups and scaleups need flexible engineers who can own the stack end-to-end, while large manufacturers seek specialists for each stage of the chip lifecycle.
Top Programming & Scripting Languages for Semiconductor Roles
1. Verilog / VHDL
What it is: Hardware description languages used to model digital circuits.
Why it matters: Still the foundation of FPGA development and ASIC design.
Used by: ARM, Imagination, aerospace contractors, telecoms.
Roles: RTL Engineer, FPGA Designer, ASIC Logic Designer.
Skills to pair: Testbenches, waveform analysis, constraints, FPGA toolchains.
2. SystemVerilog + UVM
What it is: Industry-standard verification language and methodology.
Why it matters: Enables robust simulation, testbench creation, coverage-driven development.
Used by: IP vendors, SoC teams, foundry customers.
Roles: Verification Engineer, Functional Test Developer.
Skills to pair: Constrained random testing, functional coverage, SV classes.
3. Python / Tcl / Shell
What it is: Scripting languages used to automate chip design flows.
Why it matters: Speeds up regression testing, synthesis, timing analysis, and DRC/LVS checks.
Used by: EDA teams, P&R engineers, backend specialists.
Roles: CAD Engineer, Flow Developer, Physical Design Engineer.
Skills to pair: EDA tool APIs, file parsing, metrics dashboards.
4. C / C++
What it is: High-level languages used for firmware and chip-software integration.
Why it matters: Bridges silicon with real-world embedded systems.
Used by: Automotive electronics, AI accelerator teams.
Roles: Embedded Engineer, Hardware-Software Integration Specialist.
Skills to pair: Memory mapping, MMIO, interrupt handling.
Core EDA Tools & Design Workflows
1. Cadence Tool Suite
Tools: Virtuoso (analogue/mixed-signal), Genus (synthesis), Innovus (P&R).
Why it matters: Full RTL-to-GDSII flow, used in commercial tape-outs.
Used by: NXP, Samsung Foundry, UK startups.
Skills to pair: Timing closure, DRC/LVS debugging, schematic/layout co-design.
2. Synopsys Flow
Tools: Design Compiler, IC Compiler II, PrimeTime, VCS.
Why it matters: Preferred in many Tier 1 silicon design teams.
Roles: Logic Designer, STA Engineer, Verification Specialist.
Skills to pair: Netlist synthesis, constraint management, static timing analysis.
3. SPICE Simulation
Tools: HSPICE, Spectre, Eldo, LTspice.
Why it matters: Essential for validating analogue/mixed-signal performance.
Used by: Analogue teams, RF engineers, power IC designers.
Roles: Analogue Design Engineer, Mixed-Signal Modeller.
Skills to pair: Netlist generation, model libraries, corner simulations.
4. Layout & Verification
Tools: Calibre, PVS, Pegasus.
What it is: Physical verification for DRC, LVS, and parasitic extraction.
Used by: Tape-out teams, foundries, backend engineers.
Roles: Layout Engineer, Tape-out Coordinator.
5. FPGA Tools
Vendors: Xilinx Vivado, Intel Quartus, Lattice Radiant.
Use case: Prototyping, embedded acceleration, rapid hardware deployment.
Used by: Defence contractors, medtech, AI hardware startups.
Skills to pair: Timing constraints, floorplanning, IP integration.
Fabrication, Process & Packaging Techniques
1. Cleanroom Operations
Techniques: Photolithography, etching, ion implantation, spin coating.
Roles: Process Engineer, Device Fabrication Technician.
Used by: IQE, Pragmatic, academic fabs.
2. Deposition & Etching Equipment
Tools: CVD, ALD, PVD, RIE.
Why it matters: Core to front-end wafer processing.
Used by: Compound semiconductor labs, MEMS foundries.
3. Failure Analysis & Reliability Testing
Tools: SEM, FIB, X-ray imaging, microprobing, BERT.
Used by: Yield engineers, QA teams.
Roles: Reliability Test Engineer, Product Assurance Analyst.
4. IC Packaging & Assembly
Techniques: Flip-chip, WLCSP, 2.5D interposers, wire bonding.
Used by: Backend assembly houses, AI chipmakers.
Roles: Packaging Engineer, Thermal Analysis Engineer.
Emerging Semiconductor Technologies
1. RISC-V Architecture
Why it matters: Custom CPUs for IoT, edge, security, and AI.
Used by: SiFive partners, embedded system designers.
Skills to pair: Open-source cores, toolchain setup, ISA extensions.
2. GaN & SiC Power Devices
Why it matters: Enable compact, high-efficiency power solutions.
Used by: EV makers, aerospace, energy.
Roles: Power Device Designer, Applications Engineer.
3. Silicon Photonics
Use case: High-speed optical interconnects in datacentres and quantum computing.
Tools: Lumerical, IPKISS.
Roles: Photonic IC Designer, Optical Packaging Engineer.
4. AI-Driven EDA Tools
Examples: Synopsys DSO.ai, Cadence Cerebrus.
Why it matters: ML-assisted layout, timing, and power optimisation.
Roles: EDA Automation Engineer, ML Flow Specialist.
5. Chiplet Integration
What it is: Modular assembly of specialised dies.
Used by: Advanced packaging teams, high-performance compute designers.
Skills to pair: Interconnect standards (UCIe), 2.5D/3D integration
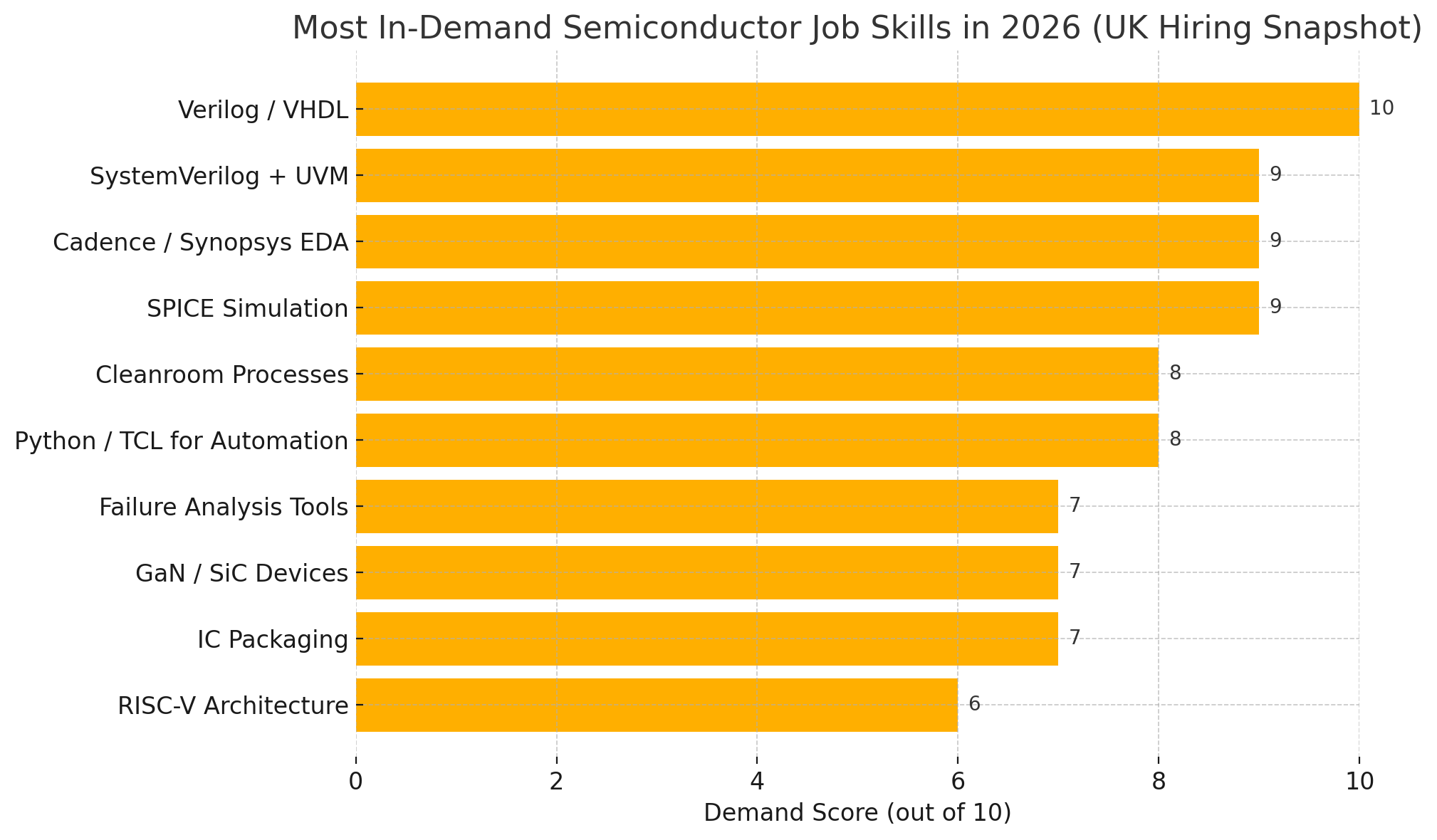
Most In-Demand Semiconductor Job Skills in 2026 (UK Hiring Snapshot Forecast)
Here’s a visual overview of the platforms, languages & tools UK employers are prioritising in chip design, process engineering, and verification roles:
How to Future-Proof Your Semiconductor Career in 2026
Get Fluent in RTL & Verification
Learn Verilog, SystemVerilog and UVM—these remain essential across ASIC and FPGA roles.Practice EDA Tools & Scripting
Master tools like Cadence Genus, Virtuoso, and Synopsys Design Compiler—and automate your flows with Python or TCL.Understand Fab & Failure Analysis Tools
Cleanroom experience and familiarity with SEM/FIB/RIE tools will set you apart in physical process roles.Follow Emerging Technologies
Gain exposure to silicon photonics, wide bandgap devices, and chiplet integration.Engage with UK Ecosystem & Funding
Join NMI (TechWorks), UKRI Semiconductor groups, and semiconductor innovation hubs in Cambridge, Newport and Sheffield.
Where to Find Semiconductor Jobs in the UK
🔍 Visit www.semiconductorjobs.co.uk to browse UK-only roles in chip design, fab ops, test & verification, failure analysis, and embedded system ICs.
Conclusion: Your Semiconductor Career Toolkit for 2026
The semiconductor workforce of 2026 will need to blend design skills, process knowledge, and adaptability to new technologies. Whether you're working on 7nm logic, SiC power modules, or open-source CPU cores, knowing what tools are in demand is the first step.
Use this Semiconductor Jobs Skills Radar 2026 to guide your upskilling, CV focus & job search strategy. We update this every year with live market trends.
Subscribe for weekly UK semiconductor job alerts, salary data, and skills guides.


